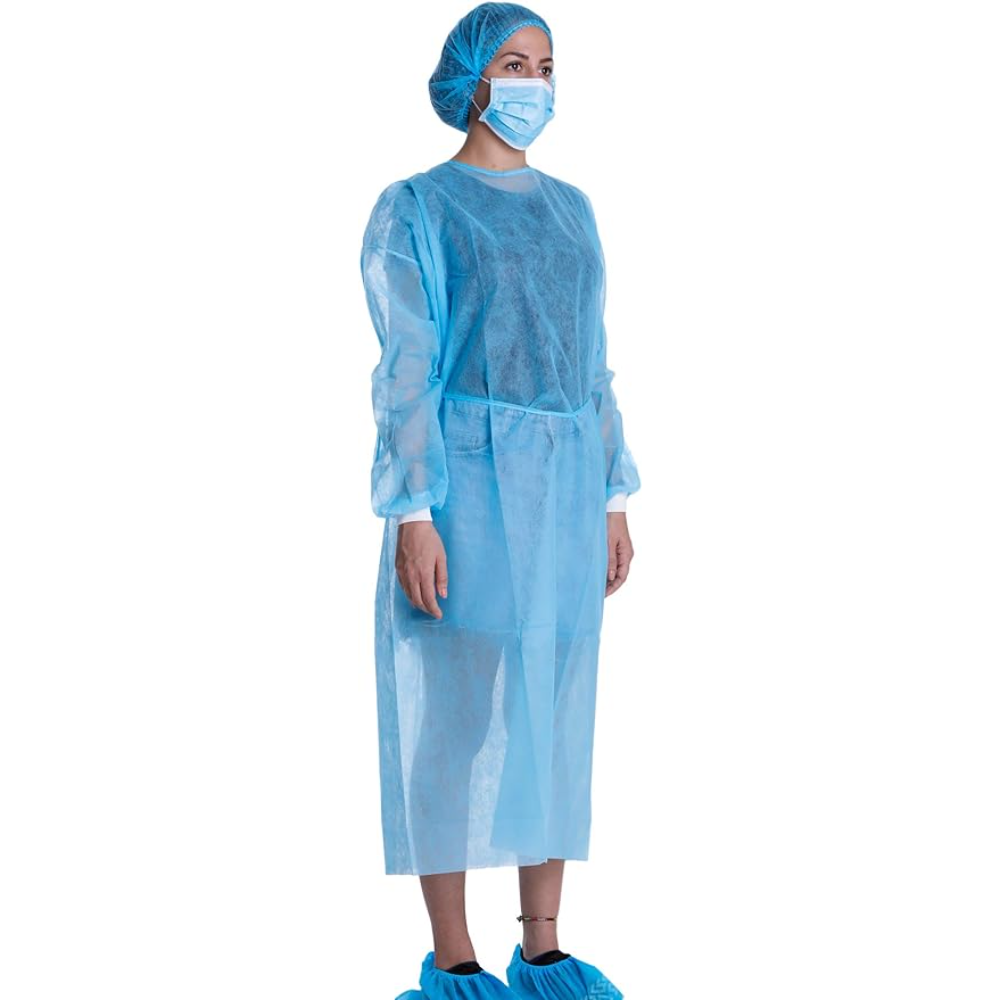
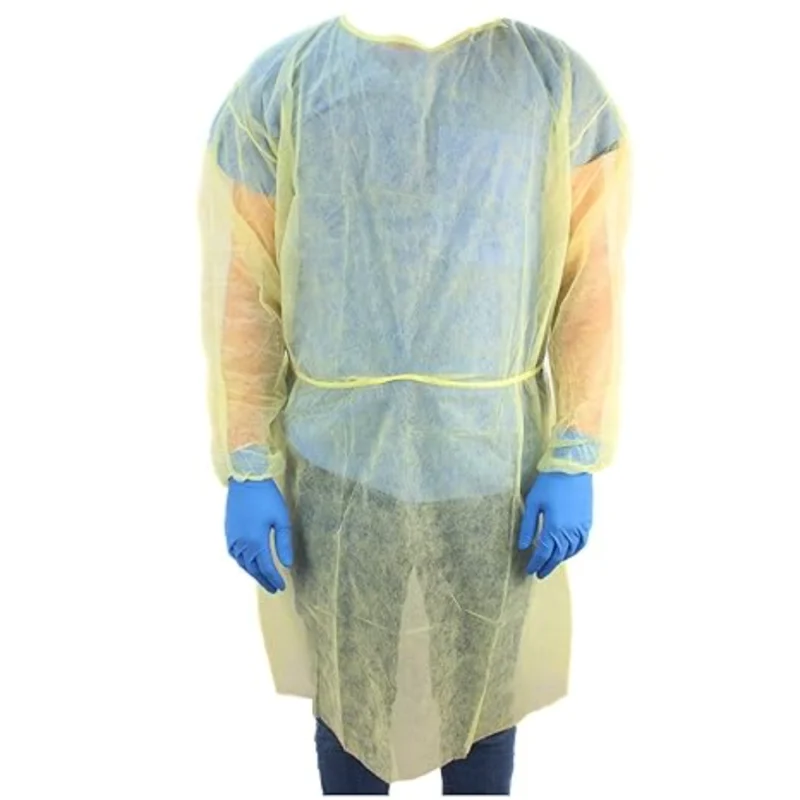
Isolation gowns are essential personal protective equipment (PPE) used primarily in healthcare settings to protect healthcare workers, patients, and visitors from the spread of infectious diseases. Here’s a detailed description of isolation gowns:
Material:
- Non-Woven Fabric: Typically made from non-woven materials like polypropylene, polyethylene, or polyester, which provide fluid resistance and breathability.
- Laminated Fabrics: Some gowns are made from fabrics laminated with polyethylene or other coatings to enhance impermeability and provide additional protection against fluids and pathogens.
Design:
- Style: Usually designed with long sleeves and full-length coverage to protect the body from neck to knees, including the back and sides.
- Closure: Features a tie or Velcro closure at the back of the neck and waist to ensure a secure fit and prevent gaps.
- Cuffs: Often include elastic or knit cuffs to ensure a snug fit at the wrists and to facilitate the use of gloves.
Types:
- Disposable Gowns: Designed for single-use to prevent cross-contamination and ensure hygiene. Made from lightweight, cost-effective materials.
- Reusable Gowns: Made from durable materials that can withstand laundering and sterilization, providing a more sustainable option for repeated use.
Levels of Protection:
- Level 1: Minimal protection, suitable for basic care and standard isolation.
- Level 2: Moderate protection, used in situations with low fluid exposure risk.
- Level 3: High protection, appropriate for procedures with moderate risk of fluid exposure.
- Level 4: Maximum protection, used in high-risk situations with significant fluid exposure and pathogen transmission risk.
Usage:
- Healthcare Settings: Worn by healthcare workers during patient care, surgical procedures, and when handling hazardous materials or infectious diseases.
- Laboratories: Used by laboratory personnel to protect against chemical splashes and biological hazards.
- Public Health Emergencies: Essential during outbreaks and pandemics to protect frontline workers and prevent the spread of infection.
Features:
- Breathability: Non-woven materials provide breathability to enhance comfort during prolonged use.
- Fluid Resistance: Designed to resist penetration by liquids and body fluids, offering protection against contamination.
- Ease of Use: Simple to don and doff, minimizing the risk of contamination during removal.
Compliance:
- Standards: Must meet specific standards and guidelines set by organizations such as the FDA, CDC, and OSHA to ensure adequate protection and safety.
Maintenance:
- Disposable Gowns: Should be disposed of immediately after use in designated biohazard containers.
- Reusable Gowns: Require proper laundering and sterilization according to manufacturer guidelines to maintain their protective properties and hygiene.